Cookie-based vs Token-based
有两种认证方式,一种是基于 cookie 的认证,另一种是基于 token 的认证。后者实现往往是通过 JSON Web Token (以下简称 JWT)实现的。首先要说明一下两种认证方式的区别:
cookie-based authentication 的认证流程是:
- 用户填写 credentials,包括用户名,邮箱,密码这些内容;
- Server 服务器验证这些 credentials 是否正确,如果正确,则认证成功,创建一个 session 存储在数据库中;
- 将这个 session 的 session id 存储在浏览器端的 cookie 里;
- 接下来的每一个请求,都会带着这个 session id,Server 在接收请求后也会验证 session id 与 session 是否匹配;
- 一旦用户登出,client 端和 server 端的 session 均被摧毁;
token-based authentication:
- 用户填写 credentials,包括用户名,邮箱,密码;
- Server 服务器验证这些 credentials 是否正确,如果认证成功,则返回一个 signed token;
- 这个 token 会被存储在 client 端,大部分是在 localStorage,但也会存储在 session storage 或是 cookie 里;
- 接下来的每一个请求,都会带着 token 作为额外的 authentication 信息。
- Server 收到请求后,首先 decode 这个 token 并对 token 里的 signature 进行验证;
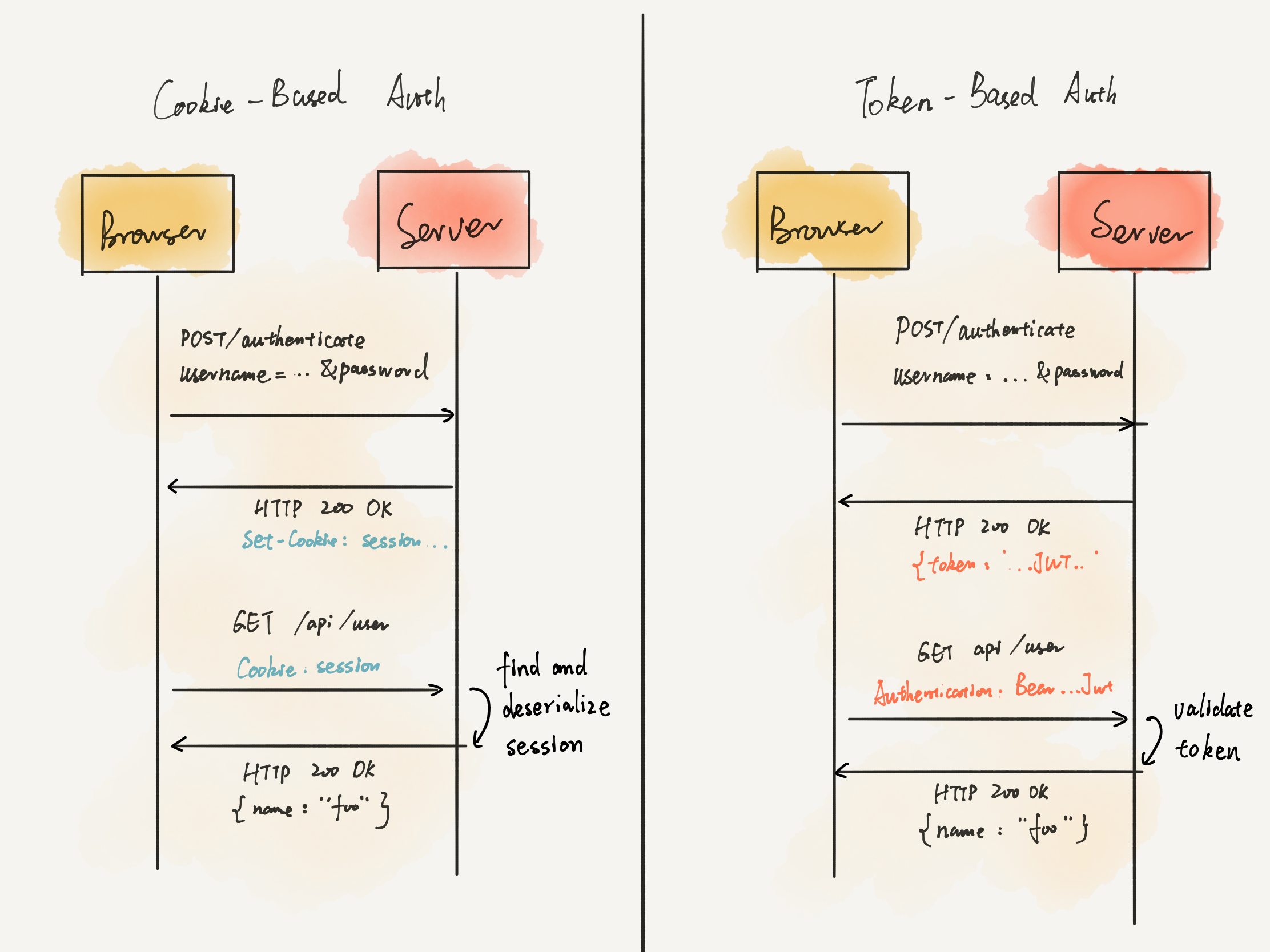
为什么会说 token-based 更好:
- stateless,也就是不需要再在 server 端保存一份纪录,但 server 端要保存用于签名时用的「secret key」;
- cookie 对跨域 CORS 操作不友好,token 则没有这个问题;
JWT 如何产生的
一条完整的 JWT 格式是这样的:header.payload.signature。
第一步,创建一个 JSON 格式的 header。header 里包含的信息需要有这个 JSON 使用的 hash 算法,例如:
const header = {
typ: "JWT",
alg: "HS256"
}
"typ" 声明这是一个 JWT,"alg" 声明所有是用的 hash 算法;
第二步,创建 payload。这里的 payload 就是你想在 JWT 里存储的任何数据信息,但最好不要把敏感信息,比如密码放在里面,
const payload = {
userId: "b08f86af-35da-48f2-8fab-cef3904660bd"
}
对于 JWT 的 payload,会有一些标准,比如 iss 代表 issuer,sub 代表 subject,exp 代表 expiration time。
第三步,创建 signature 签名。
const encodedHeader = Buffer.from(JSON.stringify(header)).toString('base64')
const encodedPayload = Buffer.from(JSON.stringify(payload)).toString('base64')
将 header 和 payload 都使用 base64 编码。
const crypto = require('crypto')
const jwtSecret = 'secretKey'
const signature = crypto.createHmac('sha256', jwtSecret).update(encodedHeader + '.' + encodedPayload).digest('base64')
base64 编码后的文本使用 . 连接,再进行 hash,hash 后的文本再进行 base64 编码。
最终 JWT 为:
const jwt = `${encodedHeader}.${encodedPayload}.${signature}`
JWT 的认证
The very important thing to note here is that this token is signed by the HMACSHA256 algorithm, and the header and payload are Base64URL encoded, it is not encrypted. If I go to jwt.io, paste this token and select the HMACSHA256 algorithm, I could decode the token and read its contents. Therefore, it should go without saying that sensitive data, such as passwords, should never be stored in the payload.
一定要区分认证和加密,JWT 不会加密混淆数据。当用户成功登录,服务器端按照上述过程生成一条 JWT 返回给了客户端。因为 JWT 涉及到了身份认证,还是很敏感的,客户端把这个 JWT 存储在 HttpOnly Cookie,不同于传统 cookie,标有 HttpOnly 的 cookie 只能由 Server 端获取。
登录成功后,当需要请求某个需要权限的 api 或是进入某个 route 时,client 端在发送 request 请求就会把这个 JWT 稍带着,通常是在 Authorization 里,以 Bearer 作为开头:
Authorization: Bearer <token>
服务器收到请求后,首先需要验证这个 token。验证 JWT 包含以下几个步骤:
- 验证 JWT 的格式是否正确;
- 验证 signature 签名;
- 验证在 payload 里的 standard claims;
- 验证许可权限范围;
在验证 signature 时,具体是先使用 base64 decode 整个 JWT,获得 header 和 payload 的内容。在 header 里能找到 JWT 使用的 hash 算法。使用该 hash 算法和本来就在服务器端存储的 secret key ,重复一遍上面的流程,比较结果和 JWT 中的 signature 是否匹配。
The API needs to check if the algorithm, as specified by the JWT header (property
alg), matches the one expected by the API. If not, the token is considered invalid and the request must be rejected.To check if the signature matches the API’s expectations, you have to decode the JWT and retrieve the
algproperty of the JWT header.Remember that the signature is created using the header and the payload of the JWT, a secret and the hashing algorithm being used (as specified in the header: HMAC, SHA256 or RSA). The way to verify it, depends on the hashing algorithm:
在 express 里实际应用
Node.js API Authentication With JWT
这个视频 step-by-step 讲解了如何在 express 里使用 jsonwebtoken 这个 package,以下是最终完整代码:
const express = require('express');
const jwt = require('jsonwebtoken');
const app = express();
app.get('/api', (req, res) => {
res.json({
messgae: 'welcome to the api'
})
});
app.post('/api/posts', verifyToken, (req, res) => {
jwt.verify(req.token, 'secretkey', (err, authData) => {
if (err) {
res.sendStatus(403);
} else {
res.json({
message: 'post created ...',
authData
})
}
})
})
app.post('/api/login', (req, res) => {
// Mock user
const user = {
id: 1,
usernmae: 'brad',
email: '[email protected]'
}
jwt.sign({user}, 'secretkey', (err, token) => {
res.json({
token
})
});
});
// Format of Token
// Authorization: Bearer <access_token>
// Verify Token
function verifyToken(req, res, next) {
// Get auth header value;
const bearerHeader = req.headers['authorization'];
// Check if bearer is undefined
if (typeof bearerHeader !== 'undefined') {
// Split at the space
const bearer = bearerHeader.split(' ');
// Get token from array
const bearerToken = bearer[1];
// Set the token
req.token = bearerToken;
// Next middleware
next();
} else {
// Forbidden
res.sendStatus(403);
}
}
app.listen(5000, () => console.log('server started on 5000'))
通过 jwt.sign() 进行签名。
函数 verifyToken 仅仅是作为一个 middleware 去 retrieve header 里的 token,并把它保存在 req.token 里,具体的认证是通过 jwt.verify() 实现的。
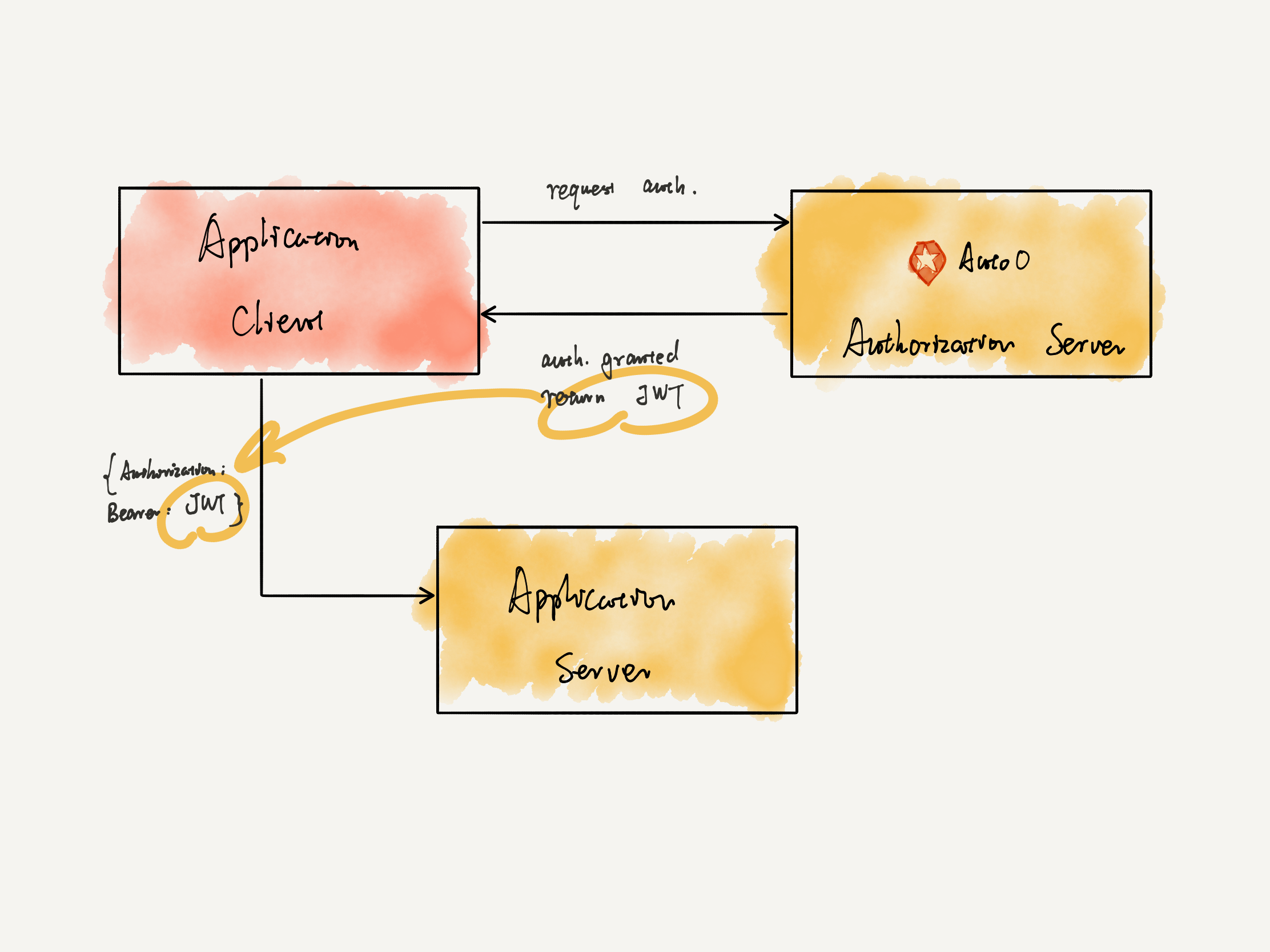
HS256 vs RS256
前者是对称加密,只有一个 key 值。后者 RS256 是非对称加密,有一个 private key 和一个 public key。上文仅仅提到了 HS256 的认证过程,但如果使用非对称加密(也更推荐这种方式)来生成 JWT,认证时需要用到 JSON Web Key Set。
For
RS256, the tenant’s JSON Web Key Set (JWKS) is used. Your tenant’s JWKS ishttps://YOUR_DOMAIN/.well-known/jwks.json.
通过 private key 来生成 JWT,再通过 public key 对 JWT 进行验证。在使用 RS256 非对称加密时,我们可以想象有两个 Server 端,一个是 Authentication Server,进行认证,并使用 private key 产生 JWT。另一个是 Application Server,获得来自 Authentication Server 的 public key,可以对经过Authentication Server 产生的 JWT 进行验证。
参考:
